Red Bank Architecture
Each Red Bank is a peer-to-peer, decentralized, autonomous token lending/borrowing smart contract deployed to a particular Outpost.
Key participants in the Red Bank's dynamic functioning include:
- Validators/Stakers: Stake$ MARS on Mars Hub, secure the Mars Hub network, govern Outposts, implement new features and set risk parameters. In return for doing so, they earn a portion of protocol revenues.
- Lenders: Lenders deposit tokens into the Red Bank to earn token rewards (sometimes described as 'yield' or an 'interest rate' or 'APR/APY') that are ultimately funded by token borrowers.
- Ordinary Borrowers: Ordinary borrowers are Red Bank lenders who also choose to borrow tokens from the Red Bank. They do this using their Red Bank deposits as collateral.
- C2C Borrowers: C2C Borrowers are smart contract systems on an Outpost that have been approved by the Martian Council to 'borrow' tokens from that Outpost's Red Bank on a contract-to-contract ("C2C") basis. Unlike human Red Bank borrowers, C2C Borrowers do not need to overcollateralize their loans from the Red Bank with matching deposits into the Red Bank--instead, due to pre-programmed compatibility between the Red Bank and a liquidation engine for the borrowing smart contract system, the Red Bank holds an indirectly 'smart lien' on the borrowed tokens such that the borrowed tokens can be liquidated from the C2C Borrower and the proceeds of that liquidation paid to the Red Bank to maintain the Red Bank's solvency.
- Liquidators: Third parties that liquidate Red Bank positions by repaying the debt of under-collateralised users in exchange for a fee. Liquidators can also liquidate C2C Borrowers (specifically, in the current architecture, the C2C Borrowers known as "Rovers") that have fallen below their required LTV ratios, and will pay the proceeds of such liquidations back to the Red Bank as well.
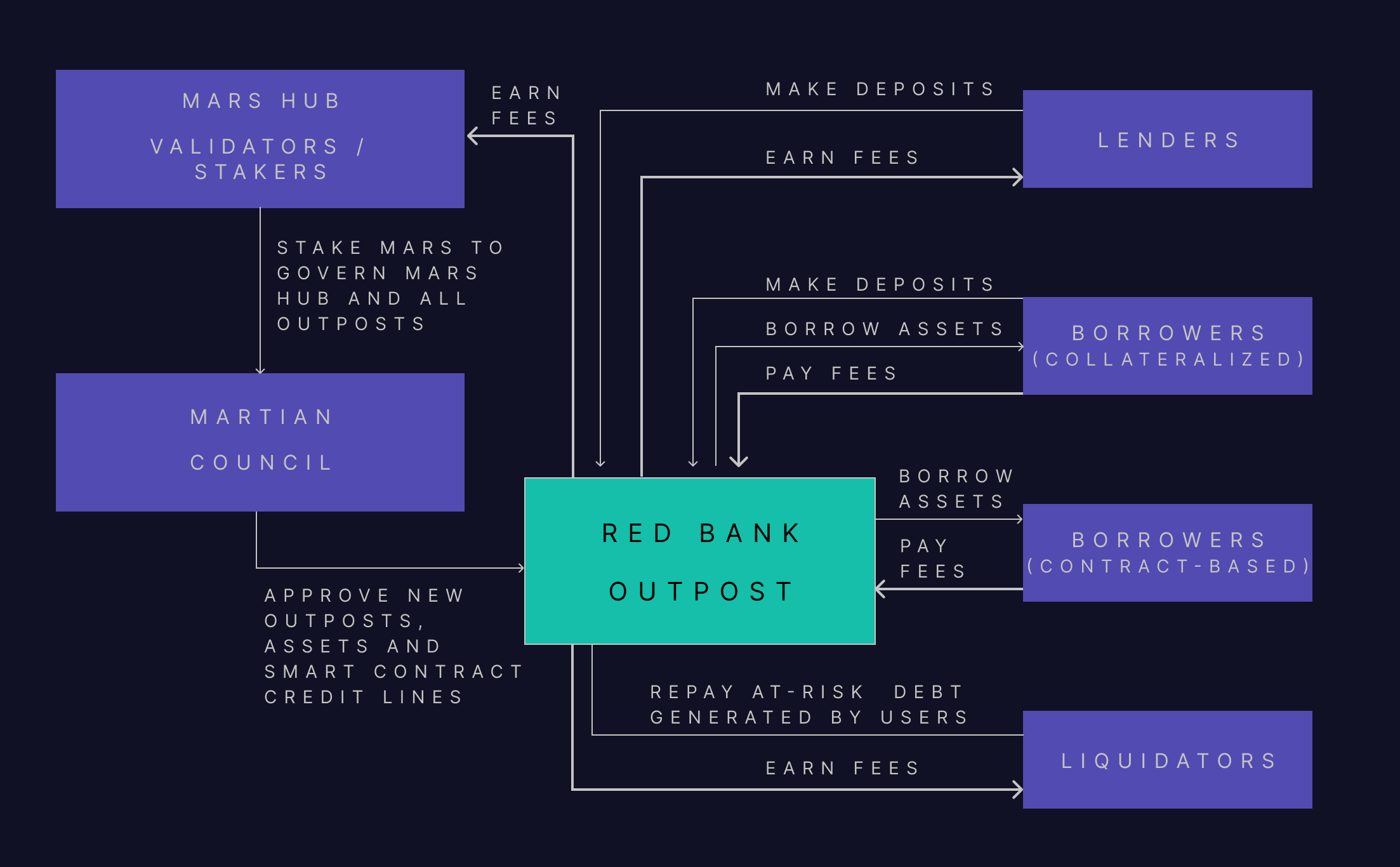
Each deployment of the Red Bank for a given outpost is comprised of the following stakeholders:
-
Validators/Stakers: Stake MARS on Mars Hub, secure the Mars Hub network, govern outposts, implement new features and set risk parameters. In return for doing so, they earn a portion of protocol revenues.
-
Lenders: Deposit assets into Mars liquidity pools, earning a fee analogous to an interest rate.
-
Borrowers (collateralised): Borrow assets from Mars liquidity pools using their deposited assets as collateral. These borrowers must, therefore, also be depositors.
-
Borrowers (contract-based): Smart contracts that are whitelisted to borrow assets from Mars liquidity pools without posting collateral (as the contracts themselves will hold collateral). Each smart contract must be approved by governance, with a set credit limit to mitigate the protocol’s risk exposure. These credit lines power Mars’ credit accounts, giving end users access to leverage without first requiring Red Bank deposits.
-
Liquidators: Third parties that liquidate Red Bank positions by repaying the debt of under-collateralised users in exchange for a fee